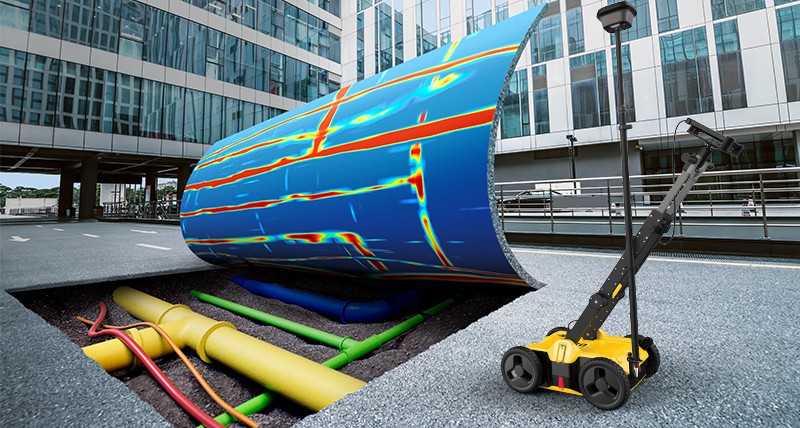
Utility surveys play a vital role in identifying, mapping, and maintaining the vast network of underground infrastructure that supports modern urban environments. Traditional methods often involve invasive excavation, leading to disruption, delays, and increased costs. However, Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) has emerged as a game-changing technology that allows for non-invasive, accurate, and efficient mapping of utilities beneath the ground. GPR utilizes radar pulses to create images of the subsurface, detecting a range of utilities from water pipes to electrical cables, without the need for digging.
What is Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)?
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to detect and subsurface mapping features. When GPR is deployed, it emits a radar signal into the ground. This signal then travels through different layers of soil, rock, or other materials. When the signal encounters an interface between different materials (such as between a utility pipe and the surrounding soil), it reflects back to the GPR antenna. The system then processes these reflected signals to create an image of what’s beneath the surface.
Market Size and Growth:
Market Size: The global utility survey market is expanding rapidly. With the increasing complexity of underground infrastructure, demand for precise mapping tools is growing. Key users of GPR for utility surveys include construction companies, city municipalities, utility providers, and infrastructure maintenance firms. In Bangladesh its major user are LGED, PWD, WASA, RAJUK, City Corporation, DESCO, NESCO, PGCB, RHD etc.
Growth Rate: The market for utility surveys through GPR has experienced consistent growth, driven by urbanization, the need for infrastructure upgrades, and increasing focus on safety and efficiency in construction. Technological advancements in GPR equipment, data processing software, and integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are expected to fuel further expansion.
Key Technologies in Utility Survey and Mapping:
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR): GPR is the leading technology for utility mapping, offering real-time imaging of underground structures. It works by emitting high-frequency electromagnetic pulses into the ground, which reflect off subsurface objects and return to the GPR antenna. This data is then used to map utilities like water pipes, electrical cables, and gas lines, with high accuracy.

Electromagnetic Induction (EMI): Used to detect conductive utilities such as metal pipes and cables, EMI can sometimes be used in conjunction with GPR for more comprehensive mapping.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Though not used exclusively for utilities, LiDAR is often employed in combination with GPR to create detailed 3D maps of the ground surface and subsurface features, enhancing the overall quality of surveys.
Regional Insights:
North America: The U.S. and Canada are at the forefront of GPR technology adoption, with widespread use across urban planning, construction, and infrastructure management. The growing trend toward smart cities and advanced infrastructure maintenance fuels the demand for utility mapping services.
Europe: Countries like the UK, Germany, and France have seen an increased use of GPR for mapping utilities as part of their focus on sustainable urban development and infrastructure modernization.
Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization in countries like China, India, Bangladesh and Japan has created significant demand for GPR in utility surveys. The need for accurate underground utility mapping in densely populated cities drives the growth of this market.
South America: Brazil, Chile, and Argentina are embracing GPR for utility detection in major infrastructure projects, particularly in urban development and mining.
QC LAB SERVICE: Role in Utility Survey and GPR Service
As a leading provider of utility surveys in Bangladesh, QC LAB Service. has the opportunity to leverage GPR technology to offer precise and reliable mapping services to government and private sector clients alike. By integrating advanced technologies with local expertise, QC LAB Service. plays a key role in both enhancing infrastructure safety and supporting Bangladesh’s growing demand for modern utility mapping and management solutions.
Bridging International Techniques
QC LAB Service. Brings international best practices in utility survey and mapping to Bangladesh by:
Adopting and Customizing GPR Technology: Utilize the latest GPR systems and integrate them with local surveying practices to ensure accuracy and efficiency in utility mapping.
Training and Knowledge Transfer: Organize workshops for local engineers and surveyors, ensuring they are well-versed in using GPR equipment and interpreting the results accurately.
Collaborative Projects: Work with international firms and institutions to bring cutting-edge GPR techniques and data analytics to the Bangladesh market.
Contributing to Digital Bangladesh:
QC LAB Service. can support the vision of a Digital Bangladesh through the integration of utility survey and mapping data into digital platforms. Here’s how:
Geospatial Data Integration: By integrating utility mapping data from GPR surveys into GIS and digital databases, QC LAB Service. contributes to a more comprehensive and accessible infrastructure management system.
Developing Digital Solutions: The data collected from utility surveys can be used to create software solutions or mobile applications that provide real-time updates on utility locations, making it easier for municipalities and construction teams to manage underground infrastructure.
Smart Infrastructure Planning: GPR data can assist in planning smarter cities by accurately mapping underground utilities, allowing for safer construction and infrastructure upgrades.
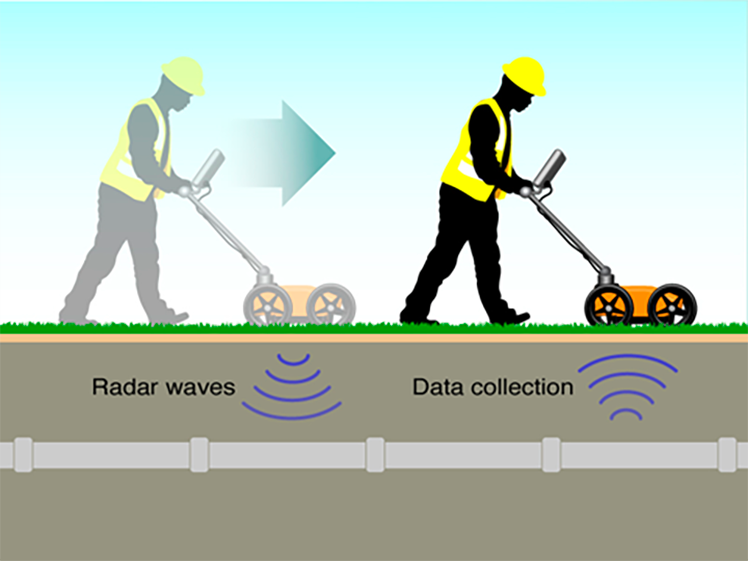
Test Procedure for GPR Utility Surveys:
Preparation: GPR survey equipment is set up and calibrated according to the specific requirements of the area, including soil conditions and the types of utilities to be surveyed.
Survey Execution: GPR is moved across the survey area, typically mounted on a cart, emitting radar pulses into the ground and collecting reflected signals.
Data Acquisition: The GPR system processes the reflected radar signals, which are analyzed to detect the location and depth of utilities.
Data Analysis: The processed data is examined by specialists, who map out the utilities and identify any potential anomalies, such as voids or damaged infrastructure.
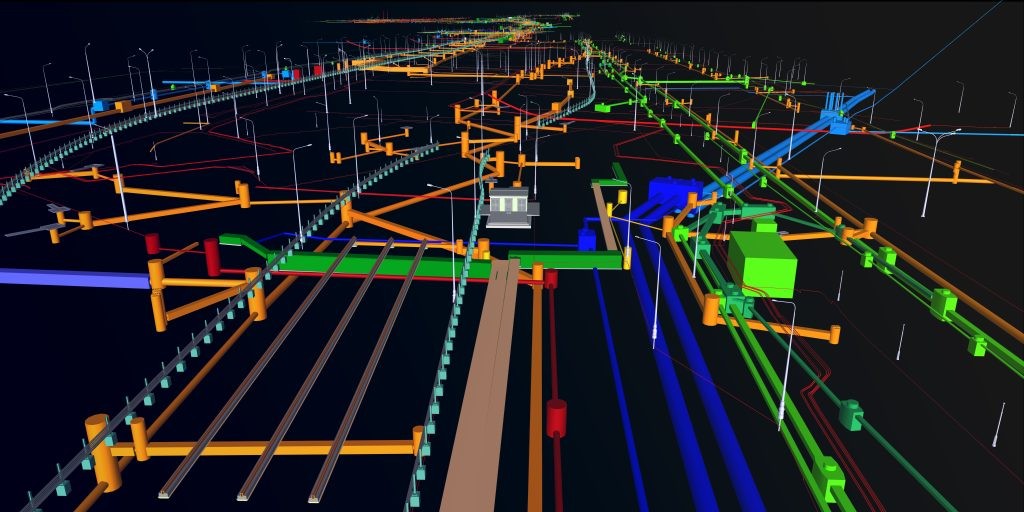
Reporting: The final report of GPR provides detailed maps and diagrams of underground utilities, including their depth, orientation, and condition, along with recommendations for further action if needed.
Advantages of Using GPR in Utility Surveys:
Non-Invasive: GPR is a non-destructive method, meaning it can map utilities without digging, minimizing disruption and reducing costs.
Real-Time Results: GPR provides instant results, allowing surveyors to make decisions quickly and avoid delays.
High Accuracy: With high-resolution imaging, GPR can accurately detect the location, depth, and type of utilities, preventing accidental damage during construction.
Cost-Effective: By reducing the need for manual excavation and avoiding utility damage, GPR saves time and money in utility surveys.
Comprehensive Coverage: GPR can detect a variety of utilities, including water, gas, electrical, and telecommunication lines, all in one survey.
Future Scope of GPR in Utility Surveying:
Advancements in Data Processing: Future developments in GPR data processing software, including machine learning and AI, will enhance the speed and accuracy of utility detection, providing even more detailed and precise maps.
Integration with Smart City Technologies: As cities move toward becoming smarter, integrating GPR data into broader urban planning frameworks, such as smart infrastructure and resource management systems, will become increasingly important.
Collaboration with Other Technologies: Combining GPR with other geophysical methods like electromagnetic induction (EMI) or LiDAR will provide a more comprehensive view of the subsurface, benefiting industries such as construction, urban development, and environmental monitoring.
Ground Penetrating Radar has revolutionized the way underground utilities are mapped, offering non-invasive, real-time, and highly accurate solutions. As urban environments grow and infrastructure demands increase, the need for precise utility mapping will continue to rise. By adopting GPR technology, QC LAB Service. will lead the charge in modernizing utility surveys in Bangladesh, contributing to safer construction practices, more efficient infrastructure management, and the realization of a Digital Bangladesh. As the market for GPR utility surveys continues to expand, the integration of advanced technologies and data solutions will provide even more opportunities for growth and innovation in the sector.

